Чувство возможности и рынок При принятии решения?
Синий краб солдат, Mictyris longicarpus, является одним из
видов, который живет в песчаных пляжах Австралии и в других местах. Взрослые в
среднем 25 мм, белый, синий цвет на спине. Они питаются отходами на пляже.
Самцы образуют большие «армии», которые движутся на пляже во время отлива, а
затем закопать в ожидании следующего отлива. Количество крабов возникает,
зависит от температуры, ветра, дождя.
Интересный факт заключается в том, что, когда они находятся
на пляже в поисках пищи должны смотреть, чтобы увидеть, если уровень моря
поднимается, потому что руководствовались "таинственным импульсом"
армия возвращается к месту отправления, чтобы снова зарываются в песок. Как вы
знаете? Приливы определяются гравитационной силой Луны, оказываемого на земле;
крабы имеют чувствительные биологические часы к этому аттракциону, так что они
"знают", когда, чтобы вернуться и снова искать защиты. Таинственное
и, казалось бы, непостижимое, но реально.
Волна представляет собой периодическое изменение уровня
моря, вызванное притяжением Луны и Солнца на Землю вместе. Явление ощутим в
море, потому что вода не является жестким и, следовательно, деформируется,
создавая видимые движения, которые изменяют уровень моря.
Приливное явление известно с древних времен. Pytheas (IV век
до н.э.). Был первым, чтобы указать на связь между амплитудой прилива и фазы
Луны, а также от частоты. Плиний Старший утверждал, что волна была связана с
луной и солнцем. Исаак Ньютон в своем Математических начал натуральной
философии ( "Математические начала натуральной философии») дал объяснение
приливов и отливов в настоящее время приняты.
Есть два известных государства: Высокий прилив или отлив,
когда вода в море достигает своей максимальной высоты в пределах цикла приливов
и отливов; Отлив или отлива противоположное состояние, где море достигает
меньшую высоту. Приблизительное время между высоким и отлива составляет 6
часов, езда на велосипеде 24 часа 50 минут. Эта периодичность является то, что
влияет на движение краба солдата, никогда не удастся.
Поток процесс идет медленно и непрерывный подъем морских
вод, путем постепенного увеличения лунного или солнечного притяжения или обоих;
Рефлюкс является медленное и постепенное снижение морских вод, в результате
распада лунного или солнечного притяжения.
Что крабы должны делать с бизнесом? Они могут быть частью
вкусного бизнеса, но и предложить интересные вещи.
Большие данные, макроданные, крупномасштабные данные или
данные масс это понятие, которое относится к хранению больших объемов данных и
процедур, используемых для поиска повторяющихся моделей, тенденции в реальном
времени.
Есть много инструментов, чтобы иметь дело с большими данными
и Hadoop, NoSQL, Кассандрой, Business Intelligence, Machine Learning и других,
любой из них некоторые из трех типов больших данных:
i) Структурированные данные. Данные, которые имеют четко
определенную длину и формат, такие как даты, числа или строки. Хранятся в
таблицах (реляционные базы данных, электронные таблицы)
ii) неструктурированные данные. формат, который остается были
собраны, они не имеют определенного формата. не могут быть сохранены в виде
таблиц, так как они не имеют базовых типов данных (PDF документы,
мультимедийные документы, электронные письма или текстовые документы).
iii) полуструктурированными данных. Данные не ограничены
определенными полями, но они имеют маркеры для разделения различных элементов.
Эти данные имеют свои собственные полуструктурированное метаданные, описывающие
объекты и отношения между ними; Они принимаются по соглашению (HTML, XML,
JSON).
В прошлом, с относительно простой и предсказуемого мира,
решения для рынка, в отношении товаров и услуг, которые могут быть предложены
для клиентов или потребителей были относительно просты и понятны, так как
некоторые данные были использованы, методы сбора они были простыми
(обследований, продаж и клиентов записи, статистические прогнозы с
использованием методов и основные инструменты, такие как линейной регрессии).
Ошибки в решениях были контролируемыми и оказывает
незначительное влияние на финансовые результаты. Потребители имели очень
ограниченный доступ к данным и доступа к информации и, следовательно, несколько
альтернатив, чтобы выбрать или несколько аргументов, чтобы быть более
требовательными. Счастливый мир для бизнеса? Может быть, но там было мало возможностей
для роста рынка и прибыльности.
Сегодня деловой мир является более сложным, потому что
потребители имеют больше доступной информации в режиме реального времени, по
объему, разнообразию, со всего мира. Решения, предпочтения, поведение и
потребление закупки отражаются в натуральном и производят явление больших
данных; это порождает лица, принимающие решения в компании должны выходить за
рамки обычного, недостаточной и устаревших средств массовой информации о том,
что теперь доступна на больших данных.
Основные описательная статистика является недостаточным и
ограниченным, теперь должны использовать прогнозирующие или предписывающих
статистические критерии и более строгие и сложные методы, но больше подходит
для данной разновидности, скорости и объема, которые характеризуют большие
данные. Нужна более трудным? Да, но есть и больше возможностей, больше рисков и
доходности в случае успеха в принятии решений.
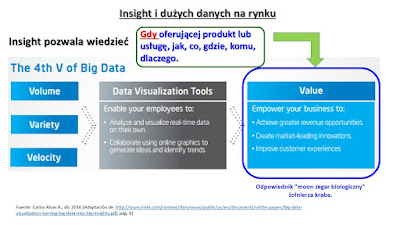
Интеллектуальная и продуктивное использование больших
объемов данных предполагает использование инструментов мощного анализа и
поддержки в области науки, научных данных, характеризуется творческим процессом
массивной данных и создания стоимости от них, значение, которое заметно
улучшает процесс принятия решений. Это значение является понимание больших данных, которые могут
действовать как «внутренний датчик» советы, когда, как, почему, что, где, кто
предлагает товар или услугу.
Решение производитель уже не может быть эмпирическим,
бухгалтер или чистый администратор, должен быть больше инженер и конечно же,
более творческим, более призрачной, но если он вздрагивает трудности, вы всегда
можете обратиться к специалистам, которые были бы подходящей поддержки. Эти
ученые данные, ученые данные, которые могут помочь создать ценность для
организации от больших данных.
Для крабы, решить, следует ли вернуться в убежище, наблюдая
приближение тела водного эквивалента к решениям исполнительной власти по
реагированию на текущем рынке, XXI века, опираясь на данные, которые
предоставляют отчеты о продажах, история клиентов, опросы (медленные,
частичные, вне времени). Оба умерли бы, если они действовали хорошо; краб
утопление и бизнесмен или исполнительной власти пожирает конкуренции.
Когда краб использует свой "биологические часы
луна" всегда точно знает, в какой момент он должен уйти в отставку со
своей «армии». Когда исполнительная власть опирается на информацию, которая
дает большие данные, он разрабатывает тщательный анализ от них и получает
соответствующее представление, имеет большой потенциал, чтобы выйти победителем
в борьбе за рынок.
ссылки
Big
Data visualización: Turning Big Data into Big insights
Big data
Marea
Mictyris
longicarpus